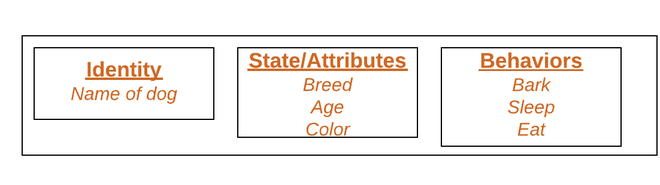
 Object-oriented programming aims to implement real-world entities like inheritance, hiding, polymorphism, etc in programming. The main aim of OOP is to bind together the data and the functions that operate on them so that no other part of the code can access this data except that function.
Object-oriented programming aims to implement real-world entities like inheritance, hiding, polymorphism, etc in programming. The main aim of OOP is to bind together the data and the functions that operate on them so that no other part of the code can access this data except that function. Many programming languages that were initially developed before OOP was popular have been augmented with object-oriented features, including Ada, BASIC, Fortran, Pascal, and COBOL.
Many programming languages that were initially developed before OOP was popular have been augmented with object-oriented features, including Ada, BASIC, Fortran, Pascal, and COBOL. Discover all about Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): key components, core principles and essential OOP concepts.
Discover all about Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): key components, core principles and essential OOP concepts.